E-mail and other application
SMTP (Email)
- SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
- SMTP is a set of communication guidelines that allow software to transmit an electronic mail over the internet is called Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
- It is a program used for sending messages to other computer users based on e-mail addresses.
- It provides a mail exchange between users on the same or different computers, and it also supports:
- It can send a single message to one or more recipients.
- Sending message can include text, voice, video or graphics.
- It can also send the messages on networks outside the internet.
- The main purpose of SMTP is used to set up communication rules between servers. The servers have a way of identifying themselves and announcing what kind of communication they are trying to perform. They also have a way of handling the errors such as incorrect email address. For example, if the recipient address is wrong, then receiving server reply with an error message of some kind.
Components of SMTP
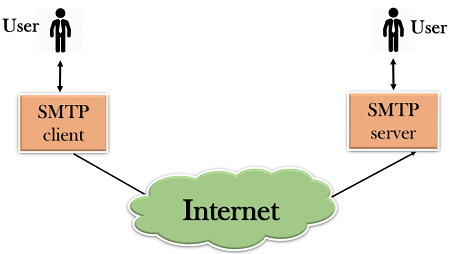
- First, we will break the SMTP client and SMTP server into two components such as user agent (UA) and mail transfer agent (MTA). The user agent (UA) prepares the message, creates the envelope and then puts the message in the envelope. The mail transfer agent (MTA) transfers this mail across the internet.
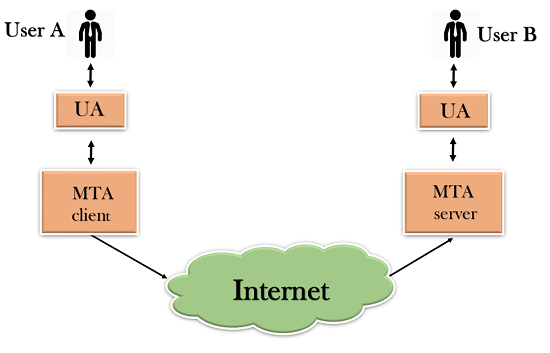
- SMTP allows a more complex system by adding a relaying system. Instead of just having one MTA at sending side and one at receiving side, more MTAs can be added, acting either as a client or server to relay the email.
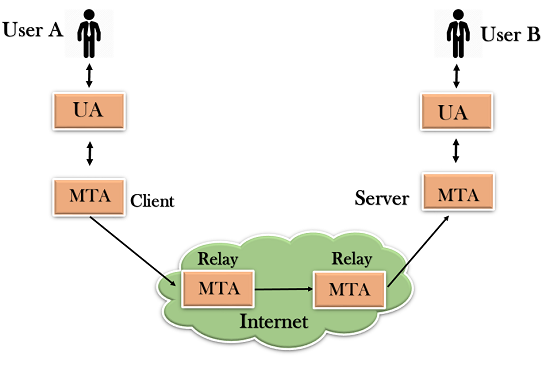
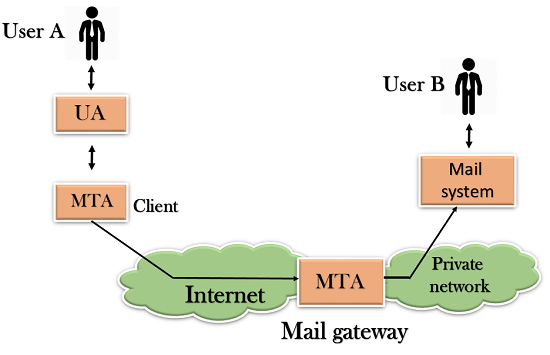
- The relaying system without TCP/IP protocol can also be used to send the emails to users, and this is achieved by the use of the mail gateway. The mail gateway is a relay MTA that can be used to receive an email.
Working of SMTP
- Composition of Mail: A user sends an e-mail by composing an electronic mail message using a Mail User Agent (MUA). Mail User Agent is a program which is used to send and receive mail. The message contains two parts: body and header. The body is the main part of the message while the header includes information such as the sender and recipient address. The header also includes descriptive information such as the subject of the message. In this case, the message body is like a letter and header is like an envelope that contains the recipient's address.
- Submission of Mail: After composing an email, the mail client then submits the completed e-mail to the SMTP server by using SMTP on TCP port 25.
- Delivery of Mail: E-mail addresses contain two parts: username of the recipient and domain name. For example, vivek@gmail.com, where "vivek" is the username of the recipient and "gmail.com" is the domain name.
If the domain name of the recipient's email address is different from the sender's domain name, then MSA will send the mail to the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA). To relay the email, the MTA will find the target domain. It checks the MX record from Domain Name System to obtain the target domain. The MX record contains the domain name and IP address of the recipient's domain. Once the record is located, MTA connects to the exchange server to relay the message. - Receipt and Processing of Mail: Once the incoming message is received, the exchange server delivers it to the incoming server (Mail Delivery Agent) which stores the e-mail where it waits for the user to retrieve it.
- Access and Retrieval of Mail: The stored email in MDA can be retrieved by using MUA (Mail User Agent). MUA can be accessed by using login and password.
FTP
- FTP stands for File transfer protocol.
- FTP is a standard internet protocol provided by TCP/IP used for transmitting the files from one host to another.
- It is mainly used for transferring the web page files from their creator to the computer that acts as a server for other computers on the internet.
- It is also used for downloading the files to computer from other servers.
Objectives of FTP
- It provides the sharing of files.
- It is used to encourage the use of remote computers.
- It transfers the data more reliably and efficiently.
DNS
An application layer protocol defines how the application processes running on different systems, pass the messages to each other.- DNS stands for Domain Name System.
- DNS is a directory service that provides a mapping between the name of a host on the network and its numerical address.
- DNS is required for the functioning of the internet.
- Each node in a tree has a domain name, and a full domain name is a sequence of symbols specified by dots.
- DNS is a service that translates the domain name into IP addresses. This allows the users of networks to utilize user-friendly names when looking for other hosts instead of remembering the IP addresses.
- For example, suppose the FTP site at EduSoft had an IP address of 132.147.165.50, most people would reach this site by specifying ftp.EduSoft.com. Therefore, the domain name is more reliable than IP address.
Telnet
- The main task of the internet is to provide services to users. For example, users want to run different application programs at the remote site and transfers a result to the local site. This requires a client-server program such as FTP, SMTP. But this would not allow us to create a specific program for each demand.
- The better solution is to provide a general client-server program that lets the user access any application program on a remote computer. Therefore, a program that allows a user to log on to a remote computer. A popular client-server program Telnet is used to meet such demands. Telnet is an abbreviation for Terminal Network.
- Telnet provides a connection to the remote computer in such a way that a local terminal appears to be at the remote side.
There are two types of login:
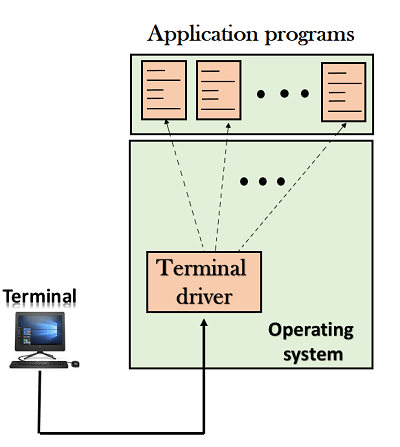
- When a user logs into a local computer, then it is known as local login.
- When the workstation running terminal emulator, the keystrokes entered by the user are accepted by the terminal driver. The terminal driver then passes these characters to the operating system which in turn, invokes the desired application program.
- However, the operating system has special meaning to special characters. For example, in UNIX some combination of characters have special meanings such as control character with "z" means suspend. Such situations do not create any problem as the terminal driver knows the meaning of such characters. But, it can cause the problems in remote login.
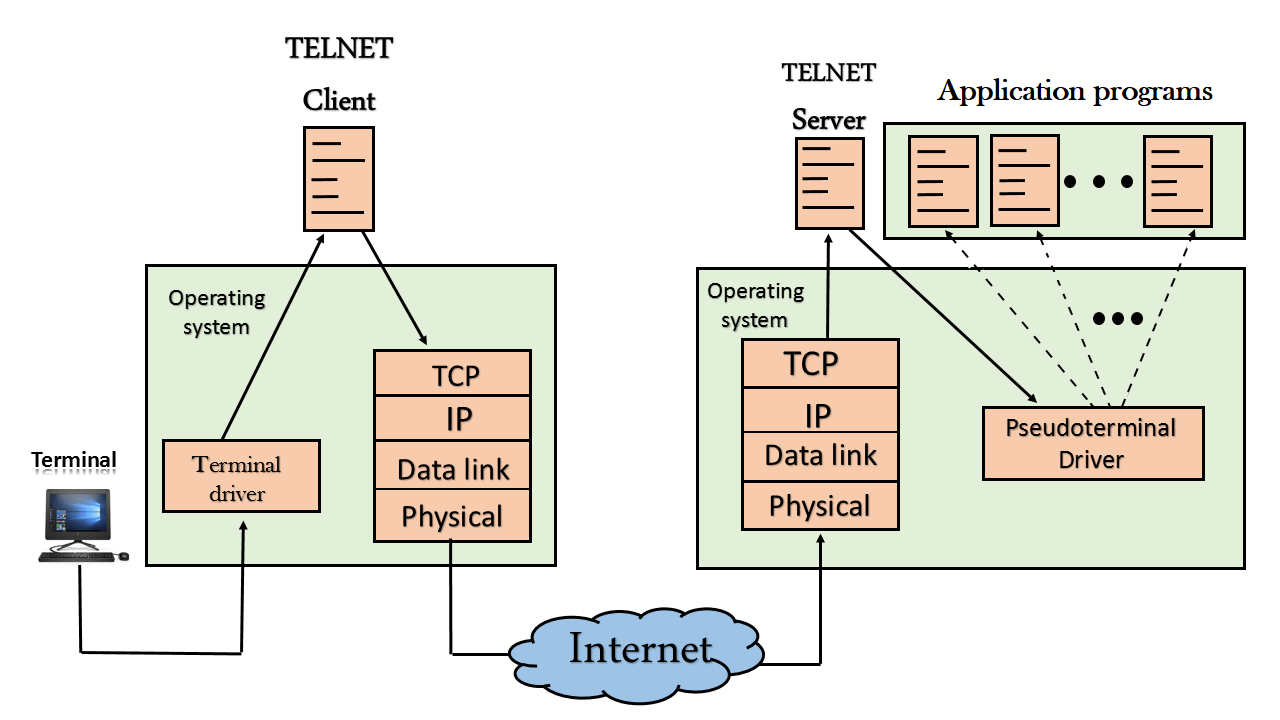
- When the user wants to access an application program on a remote computer, then the user must perform remote login.
- The network virtual terminal is an interface that defines how data and commands are sent across the network.
- In today's world, systems are heterogeneous. For example, the operating system accepts a special combination of characters such as end-of-file token running a DOS operating system ctrl+z while the token running a UNIX operating system is ctrl+d.
- TELNET solves this issue by defining a universal interface known as network virtual interface.
- The TELNET client translates the characters that come from the local terminal into NVT form and then delivers them to the network. The Telnet server then translates the data from NVT form into a form which can be understandable by a remote computer.
Local Login
Remote login
How remote login occurs
At the local site
The user sends the keystrokes to the terminal driver, the characters are then sent to the TELNET client. The TELNET client which in turn, transforms the characters to a universal character set known as network virtual terminal characters and delivers them to the local TCP/IP stackAt the remote site
The commands in NVT forms are transmitted to the TCP/IP at the remote machine. Here, the characters are delivered to the operating system and then pass to the TELNET server. The TELNET server transforms the characters which can be understandable by a remote computer. However, the characters cannot be directly passed to the operating system as a remote operating system does not receive the characters from the TELNET server. Therefore it requires some piece of software that can accept the characters from the TELNET server. The operating system then passes these characters to the appropriate application program.Network Virtual Terminal (NVT)
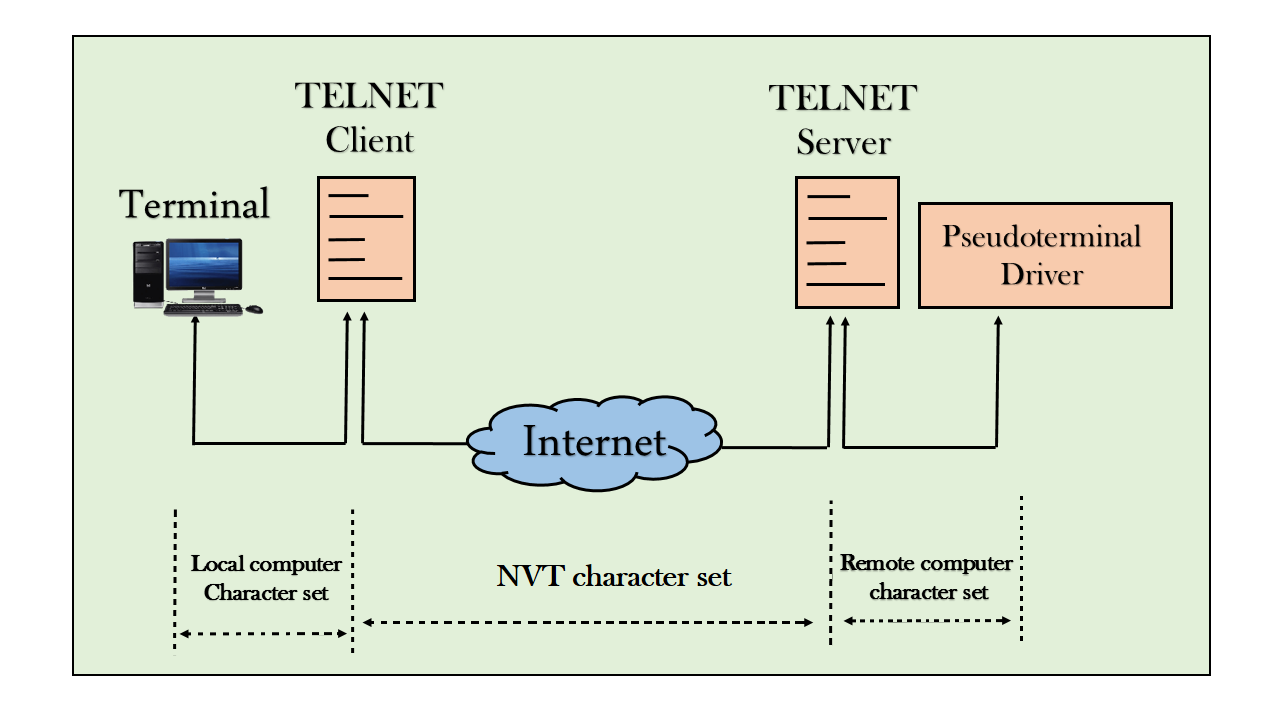
HTTP
- HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol.
- It is a protocol used to access the data on the World Wide Web (www).
- The HTTP protocol can be used to transfer the data in the form of plain text, hypertext, audio, video, and so on.
- This protocol is known as HyperText Transfer Protocol because of its efficiency that allows us to use in a hypertext environment where there are rapid jumps from one document to another document.
- HTTP is similar to the FTP as it also transfers the files from one host to another host. But, HTTP is simpler than FTP as HTTP uses only one connection, i.e., no control connection to transfer the files.
- HTTP is used to carry the data in the form of MIME-like format.
- HTTP is similar to SMTP as the data is transferred between client and server. The HTTP differs from the SMTP in the way the messages are sent from the client to the server and from server to the client. SMTP messages are stored and forwarded while HTTP messages are delivered immediately.
Features of HTTP:
- Connectionless protocol: HTTP is a connectionless protocol. HTTP client initiates a request and waits for a response from the server. When the server receives the request, the server processes the request and sends back the response to the HTTP client after which the client disconnects the connection. The connection between client and server exist only during the current request and response time only.
- Media independent: HTTP protocol is a media independent as data can be sent as long as both the client and server know how to handle the data content. It is required for both the client and server to specify the content type in MIME-type header.
- Stateless: HTTP is a stateless protocol as both the client and server know each other only during the current request. Due to this nature of the protocol, both the client and server do not retain the information between various requests of the web pages.
HTTP Transactions
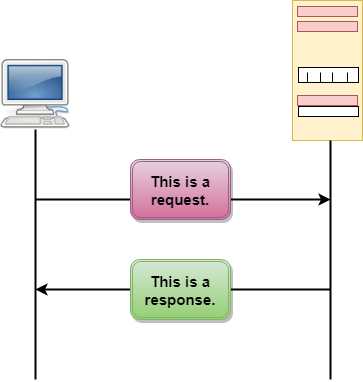
The above figure shows the HTTP transaction between client and server. The client initiates a transaction by sending a request message to the server. The server replies to the request message by sending a response message.
Messages
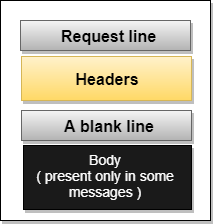
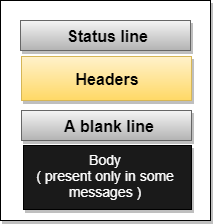
HTTP messages are of two types: request and response. Both the message types follow the same message format.
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
- A client that wants to access the document in an internet needs an address and to facilitate the access of documents, the HTTP uses the concept of Uniform Resource Locator (URL).
- The Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is a standard way of specifying any kind of information on the internet.
- The URL defines four parts: method, host computer, port, and path.

- Method: The method is the protocol used to retrieve the document from a server. For example, HTTP.
- Host: The host is the computer where the information is stored, and the computer is given an alias name. Web pages are mainly stored in the computers and the computers are given an alias name that begins with the characters "www". This field is not mandatory.
- Port: The URL can also contain the port number of the server, but it's an optional field. If the port number is included, then it must come between the host and path and it should be separated from the host by a colon.
- Path: Path is the pathname of the file where the information is stored. The path itself contain slashes that separate the directories from the subdirectories and files.